| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
- php
- AWS
- elasticsearch
- Oracle
- redis
- 요리
- Design Patterns
- JVM
- springboot
- Spring Boot
- jsp
- tool
- Git
- MySQL
- Gradle
- jenkins
- laravel
- Spring
- linux
- 맛집
- it
- ReactJS
- Spring Batch
- devops
- db
- IntelliJ
- Web Server
- ubuntu
- java
- javascript
- Today
- Total
아무거나
[reactjs] React + Typescript - 4 (React-Router) 본문
[reactjs] React + Typescript - 4 (React-Router)
전봉근 2019. 11. 19. 00:44React-Router
React-Router란
특정 URL로 유저가 접근했을 때, URL을 해석하여 기존에 개발자가 선언한대로 요청한 URL에 알맞는 React Component를 렌더링해서 보여주는 역할 Facebook 공식 라이브러리는 아니지만 React 관련 Router 라이브러리 중에서는 가장 많이 사용
React Router V4
- React Router의 최신버전
- React Router v3, 그 이하와는 API가 다름
- V3도 여전히 유지보수 진행중
- 대부분의 동작이 React Component로 이루어짐
React Router 설치하기 전에..
기존에 create-react-app이 설치되어있어야 한다.
create-react-app . --scripts-version=react-scripts-ts
lint 설정은 아래와 같이 하자.
[tslint.json]
...
"rules": {
"no-console": false,
"member-access": [true, "no-public"],
"jsx-no-lambda": false
}
React Router 설치
// react는 navtive에서도 쓰이기 때문에 별도로 분리도어있어서 dom버전을 설치하여야 한다.
yarn add react-router-dom @types/react-router-dom
React Router 사용
[App.tsx]
import * as React from 'react';
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route, } from 'react-router-dom';
import './App.css';
import logo from './logo.svg';
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<h1 className="App-title">Welcome to React</h1>
</header>
<Route path="/" render={() => <h3>Home</h3>} />
<Route path="/intro" render={() => <h3>소개</h3>} />
</div>
</Router>
);
}
}
export default App;

여기서 /intro로 접근했을 때 Home, 소개가 둘다 출력되는걸 확인할 수 있다. 왜냐하면 path에 맞는것은 전부다 render를 해준다. 즉, intro로 접근을 했지만 사실 /intro는 "/" root도 포함하는 개념이기 때문에 모두 출력해준다.
그러면 정확히 path="/"에 접근할때 정확히 해당 내용인 Home만 표시하게 하려면 exact설정을 true로 지정하자.
[App.tsx]
...
<Route exact={true} path="/" render={() => <h3>Home</h3>} />
<Route path="/intro" render={() => <h3>소개</h3>} />
...
위와 같이 지정하면 아래 이미지처럼 /intro로 접근했을때는 "소개"만 /로 접근했을때는 Home만 출력되는걸 확인할 수 있다.


Link 사용법
[App.tsx]
import * as React from 'react';
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Link, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
import './App.css';
import logo from './logo.svg';
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<div className="App">
<div className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<h1 className="App-title">Welcome to React</h1>
</div>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><Link to="/">Home</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/intro">소개</Link></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<Route exact={true} path="/" render={() => <h3>Home</h3>} />
<Route path="/intro" render={() => <h3>소개</h3>} />
</div>
</Router>
);
}
}
export default App;
위와 같이 지정하고 페이지에서 해당 Link 태그의 내용을 클릭하면 페이지이동없이 rendering 되는것을 확인할 수 있다.

Link는 실질적으론 a태그로 rendering이 된다.(개발자도구로 확인)
BrowserRouter
- 다른 라우팅 컴포넌트(Route, Link)를 사용하기 위해서 기본적으로 감싸줘야 한다.
- 오직 하나의 자식만을 가질 수 있다.
- HashRouter는 Hash(#/)로 동작하는 Router
Route
- path 속성으로 경로지정
- render, component(주로쓰임), children 속성으로 렌더링
- 실제 경로가 지정한 경로와 완벽히 매치되지 않더라도, 경로를 포함만 해도 렌더링(해결책: exact)
- 컴포넌트에 match, location, history라는 객체를 넘김
Route Component 사용법 아래 코드는 render말고 component를 사용하였을 때의 코드이다.
[App.tsx]
import * as React from 'react';
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Link, Route } from 'react-router-dom';
import './App.css';
import logo from './logo.svg';
// Component 추가
const Home = () => {
return (
<h3>Home</h3>
);
}
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<div className="App">
<div className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<h1 className="App-title">Welcome to React</h1>
</div>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><Link to="/">Home</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/intro">소개</Link></li>
</ul>
</nav>
{/* rendr -> Component로 변경 */}
<Route exact={true} path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/intro" render={() => <h3>소개</h3>} />
</div>
</Router>
);
}
}
export default App;
Link
- a태그로 렌더링되고 사용법도 비슷하나 실제 동작은 a태그와 다르게 페이지 전체를 리로드하지 않고 필요한 부분만 리로드함
React-Router-Props
파라미터 넘기는 방법
[App.tsx]
import * as React from 'react';
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Link, Route, RouteComponentProps } from 'react-router-dom';
import './App.css';
import logo from './logo.svg';
const Home = () => {
return (
<h3>Home</h3>
);
}
// Component 추가
// RouteComponentProps 제너릭에 정의한게 실제로 페이지 url에서 우리가 정의한 paramter이다.
const Post = (props: RouteComponentProps<{ postId: string }>) => {
return (
<h3>Post {props.match.params.postId}</h3>
);
}
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<div className="App">
<div className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<h1 className="App-title">Welcome to React</h1>
</div>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><Link to="/">Home</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/intro">소개</Link></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<Route exact={true} path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/intro" render={() => <h3>소개</h3>} />
{/* 파라미터를 선언한 내용 추가 */}
<Route path="/posts/:postId" component={Post} />
</div>
</Router>
);
}
}
export default App;

match
- Route 태그의 path에 정의한 것과 매치된정보를 담고 있다.
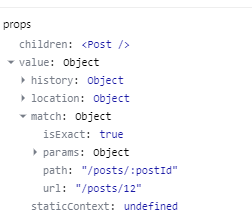
location
- 브라우저의 window.location 객체와 비슷
- URL을 다루기 쉽게 쪼개서 가지고 있음.(ex:/post/2?a=b&c=d#hash)
history
- 브라우저의 window.history 객체와 비슷
- 주소를 임의로 변경하거나 되돌아갈 수 있다.
- 주소를 변경하더라도 SPA 동작방식에 맞게 페이지 일부만 리로드(=rendering)

실습
[App.tsx]
import * as React from 'react';
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Link, Route, RouteComponentProps } from 'react-router-dom';
import './App.css';
import logo from './logo.svg';
const Home = () => {
return (
<h3>Home</h3>
);
};
const Post = (props: RouteComponentProps<{ postId: string }>) => {
// 추가
function goNextPost() {
const nextPostId = Number(props.match.params.postId) + 1;
props.history.push(`/posts/${nextPostId}`);
}
return (
<div>
<h3>Post {props.match.params.postId}</h3>
{/* 버튼추가 */}
<button onClick={goNextPost}>Next post</button>
{/* URL Paramter Parsing */}
<p>{new URLSearchParams(props.location.search).get('body')}</p>
</div>
);
};
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<div className="App">
<div className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<h1 className="App-title">Welcome to React</h1>
</div>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><Link to="/">Home</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/intro">소개</Link></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<Route exact={true} path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/intro" render={() => <h3>소개</h3>} />
<Route path="/posts/:postId" component={Post} />
</div>
</Router>
);
}
}
export default App;
이렇게 하면 페이지에서 Next Post버튼을 클릭하면 postId값이 계속 증가하는것을 확인할 수 있다.
라우팅 기능들
중첩 라우팅
PostList -> Post 로 중첩 라우팅이 되게 코드를 작성해보자.
[App.tsx]
import * as React from 'react';
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Link, Route, RouteComponentProps } from 'react-router-dom';
import './App.css';
import logo from './logo.svg';
const Home = () => {
return (
<h3>Home</h3>
);
};
const Post = (props: RouteComponentProps<{ postId: string }>) => {
function goNextPost() {
const nextPostId = Number(props.match.params.postId) + 1;
props.history.push(`/posts/${nextPostId}`);
}
return (
<div>
<h3>Post {props.match.params.postId}</h3>
<button onClick={goNextPost}>Next post</button>
<p>{new URLSearchParams(props.location.search).get('body')}</p>
</div>
);
};
// 추가
const PostList = (props: RouteComponentProps<{}>) => {
return (
<div>
<Route exact={true} path={`${props.match.url}`} render={() => <h3>postList</h3>} />
<Route path={`${props.match.url}/:postId`} component={Post} />
</div>
);
};
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<div className="App">
<div className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<h1 className="App-title">Welcome to React</h1>
</div>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><Link to="/">Home</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/intro">소개</Link></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<Route exact={true} path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/intro" render={() => <h3>소개</h3>} />
{/* 변경 */}
<Route path="/posts" component={PostList} />
</div>
</Router>
);
}
}
export default App;
http://localhost:3000/posts 로 접속했을 때

http://localhost:3000/posts/11?body=리액트라우터테스트 로 접속했을 때

Switch
<Route path={`${props.match.url}`} render={() => <h3>postList</h3>} />
<Route path={`${props.match.url}/:postId`} component={Post} />
만약 위의 코드처럼 exact=true가 없으면 http://localhost:3000/posts/11?body=리액트라우터테스트 로 접속했을 때 아래 이미지와 같이 postList도 함께 출력되는것을 볼 수 있다.

이와 같이 의도하지 않는 컴포넌트가 렌더링되는 경우에 Switch로 감싸면된다.
<Switch>
<Route path={`${props.match.url}`} render={() => <h3>postList</h3>} />
<Route path={`${props.match.url}/:postId`} component={Post} />
</Switch>
Switch란?
- Route 태그를 감싸서 사용
- Javascript의 switch 문과 비슷
- Route 태그 중 매치되는 첫번째만 렌더
- Route 태그에 path를 지정하지 않은 경우, 매치되는 Route 태그의 컴포넌트가 없을 때 렌더
따라서 순서에 유의하여야 한다.
[ 예제(404 페이지 생성) ]
[App.tsx]
import * as React from 'react';
// Switch 추가
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Link, Route, RouteComponentProps, Switch } from 'react-router-dom';
import './App.css';
import logo from './logo.svg';
const Home = () => {
return (
<h3>Home</h3>
);
};
const Post = (props: RouteComponentProps<{ postId: string }>) => {
function goNextPost() {
const nextPostId = Number(props.match.params.postId) + 1;
props.history.push(`/posts/${nextPostId}`);
}
return (
<div>
<h3>Post {props.match.params.postId}</h3>
<button onClick={goNextPost}>Next post</button>
<p>{new URLSearchParams(props.location.search).get('body')}</p>
</div>
);
};
const PostList = (props: RouteComponentProps<{}>) => {
return (
<div>
<Route exact={true} path={`${props.match.url}`} render={() => <h3>postList</h3>} />
<Route path={`${props.match.url}/:postId`} component={Post} />
</div>
);
};
// 추가
const NotFound = () => {
return (
<h3>Not Found!!</h3>
);
};
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<div className="App">
<div className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<h1 className="App-title">Welcome to React</h1>
</div>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><Link to="/">Home</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/intro">소개</Link></li>
</ul>
</nav>
{/* Switch 태그로 감쌈 */}
<Switch>
<Route exact={true} path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/intro" render={() => <h3>소개</h3>} />
<Route path="/posts" component={PostList} />
<Route component={NotFound} />
</Switch>
</div>
</Router>
);
}
}
export default App;
http://localhost:3000/sadfasfsaas 와 같이 Route path가 정의되어있지 않는곳으로 접근하면 NotFound 컴포넌트가 렌더된다. (하기 이미지 참조)

Redirect
- Redirect를 하는 컴포넌트
- 마운트 되면 지정한 경로로 이동
- 기본적으로 replace 방식
- location 객체를 통해 리다이렉트 할 수 있다.
[ 예제 Admin 페이지 ]
[App.tsx]
import * as React from 'react';
// Redirect 추가
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Link, Redirect, Route, RouteComponentProps, Switch } from 'react-router-dom';
import './App.css';
import logo from './logo.svg';
const Home = () => {
return (
<h3>Home</h3>
);
};
const Post = (props: RouteComponentProps<{ postId: string }>) => {
function goNextPost() {
const nextPostId = Number(props.match.params.postId) + 1;
props.history.push(`/posts/${nextPostId}`);
}
return (
<div>
<h3>Post {props.match.params.postId}</h3>
<button onClick={goNextPost}>Next post</button>
<p>{new URLSearchParams(props.location.search).get('body')}</p>
</div>
);
};
const PostList = (props: RouteComponentProps<{}>) => {
return (
<div>
<Route exact={true} path={`${props.match.url}`} render={() => <h3>postList</h3>} />
<Route path={`${props.match.url}/:postId`} component={Post} />
</div>
);
};
const NotFound = () => {
return (
<h3>Not Found!!</h3>
);
};
// 추가
const Admin = () => {
const isAdmin = false;
return isAdmin
? <h3>Admin</h3>
: <Redirect to="/" />
};
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<div className="App">
<div className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<h1 className="App-title">Welcome to React</h1>
</div>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><Link to="/">Home</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/intro">소개</Link></li>
<li><Link to="/admin">어드민</Link></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<Switch>
<Route exact={true} path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/intro" render={() => <h3>소개</h3>} />
<Route path="/posts" component={PostList} />
{/* 추가 */}
<Route path="/admin" component={Admin} />
<Route component={NotFound} />
</Switch>
</div>
</Router>
);
}
}
export default App;
위의 코드에서 Admin 컴포넌트의 코드만 참고하여 isAdmin의 boolean값이 바뀔때 마다 페이지가 어떻게 표시되는지 확인하자.
- isAdmin=true 일 때 http://localhost:3000/admin 접속했을 때

- isAdmin=false 일 때 http://localhost:3000/admin 접속했을 때 http://localhost:3000 로 리다이렉트 되는걸 확인할 수 있다.

Old path
오래된 페이지들을 redirect하고 싶을 때 사용
[App.tsx]
...
<Switch>
<Route exact={true} path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/intro" render={() => <h3>소개</h3>} />
{/* from이 옛날주소 to는 신주소 (즉, about -> intro로 이전) */}
<Redirect from="/about" to="/intro" />
<Route path="/posts" component={PostList} />
<Route path="/admin" component={Admin} />
<Route component={NotFound} />
</Switch>
...
이제 http://localhost:3000/about 으로 접근하면 http://localhost:3000/intro로 리다이렉트 되는것을 볼 수 있다.
NavLink
- 조금 특별한 Link 태그
- to에 지정한 path와 URL이 매칭되는 경우 특별한 스타일, 클래스를 적용할 수 있다.
주로 네비게이션에 많이 쓰는 active 스타일을 적용하기 위한 컴포넌트이다.
[App.tsx]
import * as React from 'react';
// NavLink 추가
import { BrowserRouter as Router, NavLink, Redirect, Route, RouteComponentProps, Switch } from 'react-router-dom';
import './App.css';
import logo from './logo.svg';
const Home = () => {
return (
<h3>Home</h3>
);
};
const Post = (props: RouteComponentProps<{ postId: string }>) => {
function goNextPost() {
const nextPostId = Number(props.match.params.postId) + 1;
props.history.push(`/posts/${nextPostId}`);
}
return (
<div>
<h3>Post {props.match.params.postId}</h3>
<button onClick={goNextPost}>Next post</button>
<p>{new URLSearchParams(props.location.search).get('body')}</p>
</div>
);
};
const PostList = (props: RouteComponentProps<{}>) => {
return (
<div>
<Route exact={true} path={`${props.match.url}`} render={() => <h3>postList</h3>} />
<Route path={`${props.match.url}/:postId`} component={Post} />
</div>
);
};
const NotFound = () => {
return (
<h3>Not Found!!</h3>
);
};
// true로 수정
const Admin = () => {
const isAdmin = true;
return isAdmin
? <h3>Admin</h3>
: <Redirect to="/" />
};
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<div className="App">
<div className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<h1 className="App-title">Welcome to React</h1>
</div>
<nav>
<ul>
{/* 링크를 NavLink로 변경 */}
<li><NavLink exact={true} activeStyle={{ fontSize: 24 }} to="/">Home</NavLink></li>
<li><NavLink activeStyle={{ fontSize: 24 }} to="/intro">소개</NavLink></li>
<li><NavLink activeStyle={{ fontSize: 24 }} to="/admin">어드민</NavLink></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<Switch>
<Route exact={true} path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/intro" render={() => <h3>소개</h3>} />
{/* 추가 */}
<Redirect from="/about" to="/intro" />
<Route path="/posts" component={PostList} />
<Route path="/admin" component={Admin} />
<Route component={NotFound} />
</Switch>
</div>
</Router>
);
}
}
export default App;
아래 이미지 처럼 NavLink를 클릭한것마다 폰트사이즈가 변경되는것을 확인할 수 있다.

참조
https://www.inflearn.com/course/react-with-typescript#
'Javascript & HTML & CSS > reactjs' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [reactjs] Typescript with React + Redux - 2 (redux 적용) (0) | 2019.11.19 |
|---|---|
| [reactjs] Typescript with React + Redux - 1 (프로젝트 생성) (0) | 2019.11.19 |
| [reactjs] React + Typescript - 3 (Component와 props, state) (0) | 2019.11.19 |
| [reactjs] React + Typescript - 2 (프로젝트 생성) (0) | 2019.11.19 |
| [reactjs] React + Typescript - 1 (시작하기) (0) | 2019.11.19 |





